The arrival of the Boeing AH-64E Apache Guardian marks a decisive leap in India’s airborne fire-power and joint-warfare capability. Below is a point-wise, exam-oriented breakdown covering history, contracts, technical facts, indigenous offsets, current deployment and strategic implications—followed by high-value tables for quick revision.
Key Facts at a Glance
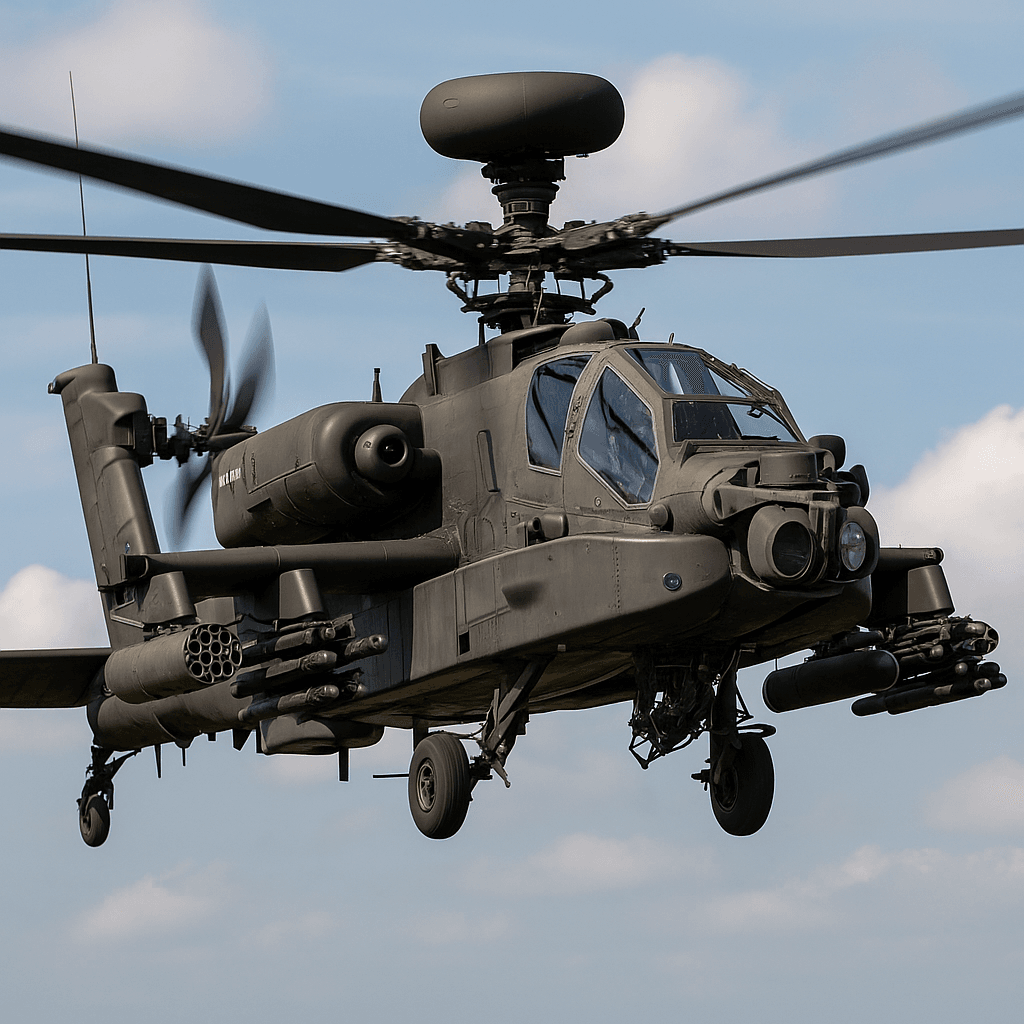
The Apache is the world’s most produced modern attack helicopter; India operates the latest AH-64E variant
Two separate programmes exist: 22 helicopters for the Indian Air Force (IAF) under a 2015 FMS/commercial deal, and 6 for the Indian Army under a 2020 FMS/commercial deal
Fuselages are manufactured in Hyderabad by Tata Boeing Aerospace Limited, making India the sole global supplier of Apache fuselages
Each Army Apache joins the newly raised 451 Army Aviation Squadron at Jodhpur near the western front
Indigenous offset clause: 30% of contract value returns to India via parts, MRO and skill development
Apache’s Longbow (AN/APG-78) mast radar tracks 128 targets, prioritises 16, and enables “fire-and-forget” missile launches
Primary weapons load: 16 AGM-114 Hellfires, 76 Hydra-70 rockets, 4 AIM-92 Stingers, and 1,200-round 30 mm M230 chain-gun
T700-GE-701D engines give 300 km/h top speed and 500 km combat radius
Manned-unmanned teaming (MUM-T) lets the Apache control Indian Heron and soon MQ-9B UAV feeds during combat
First Indian Army batch—three helicopters—landed at Hindon on 22 July 2025 after a 15-month delay; next three due by December 2025
Historical Timeline (Point-Wise)
1975-1986 – YAH-64 prototypes; Apache enters US Army service
2015 (Sep) – India signs $3 bn deal for 22 Apaches + 15 Chinook heavy-lifters (IAF)
2018 (Jun) – Tata Boeing Aerospace delivers first fuselage from Hyderabad plant
2019 (Jul-Sep) – First IAF Apaches arrive Hindon; 125 Sqn “Gladiators” stands up in Pathankot
2020 (Feb) – India orders 6 Apaches for Army; deal ~₹4,168 crore ($600 m)
2023 (Aug) – Boeing begins Mesa production for Army batch; TBAL ships first Army fuselage
2024 (Mar) – 451 Army Aviation Sqn raised at Jodhpur
2025 (Jul 22) – First three Army Apaches delivered; induction flights at Hindon
Contract, Cost & Offset Summary
| Service | Contract Year | Quantity | Value (₹/US$) | Delivery Window | Offset / Make-in-India Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Air Force | 2015 | 22 | ₹13,952 cr ≈ $3 bn | 2019-2020 | 30% offsets; simulators at Hindon; crew trained at Fort Rucker |
| Indian Army | 2020 | 6 | ₹4,168 cr ≈ $600 m | 2025 (3 + 3) | Same 30% rule; fuselages, vertical spar boxes from TBAL Hyderabad |
Strategic Significance (Point-Wise)
Dual-Service Synergy – IAF Apaches cover deep-strike and eastern high-altitude; Army Apaches provide organic anti-tank punch for strike corps in Rajasthan-Punjab deserts
Deterrence Against Armour – Hellfire tandem-warheads and precision rockets neutralise modern MBTs at standoff ranges beyond ground ATGMs
Network-Centric Ops – Link-16 data-sharing unifies Army Aviation, artillery and UAVs, shrinking sensor-to-shooter loop
Make-in-India Boost – TBAL’s 300-plus fuselage output feeds global Apache lines, adding >900 high-skill jobs and 100+ MSME suppliers
Lifecycle Support – Five-year GE Aerospace MRO contract to overaul T700 engines in country, ensuring higher fleet availability
Replacement Path – Apaches succeed ageing Mi-35; complement indigenous LCH ‘Prachand’ fleet (156 more on order) for high-altitude gunship roles
Export Credibility – India’s successful fuselage line positions Hyderabad as Boeing’s hub for future vertical-lift projects
Fast-Revision Table: Army vs Air Force Apache Squadrons
| Service | Squadron | Base | Front Covered | Callsign |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAF | 125 HU “Gladiators” | Pathankot | Western (Punjab–J&K) | Gladiators |
| IAF | 137 HU | Jorhat | Eastern (China front) | Bulldogs |
| Army | 451 Sqn | Jodhpur | Western Desert (Rajasthan) | Falcons |
Conclusion (Bullet Highlights)
Apache AH-64E delivers unmatched anti-armour capability, advanced sensors and networked warfare tools to Indian services.
Indigenous fuselage manufacturing and engine MRO underpin long-term self-reliance.
The programme exemplifies high-value offsets, joint training and twin-service synergy—key talking points for UPSC, CDS and other exams.